Azidodifluoroacetohydroxamic acid
| Cat. # | Quantity | Price | Lead time | Buy this product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAZ022_0050 | 0.05 g | 350,00 € | in stock | |
| FAZ022_0100 | 0.1 g | 650,00 € | in stock | |
| FAZ022_0250 | 0.25 g | 1.300,00 € | in stock |
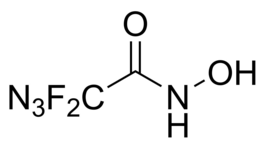
- IUPAC Name: 2-Azido-2,2-difluoro-N-hydroxyacetamide
- Synonyms: Azidodifluoroacetohydroxamic acid
- CAS: N/A
- Smiles: O=C(NO)C(F)(N=[N+]=[N-])F
- Chemical formula: C2H2F2N4O2
- Molecular weight: 152.06
- Purity: 95%+
Azidodifluoroacetohydroxamic acid introduces a fluorinated hydroxamic acid to drug candidates by click chemistry.
Owing to the electron withdrawing effect of fluorine substituents, azidodifluoroacetohydroxamic acid-derived triazoles are expected to have significantly lower pKa values than their non-fluorinated counterparts and be a good ligand for transition metals. Therefore it can be used in the design of novel metalloenzyme inhibitors.
Furthermore, when attached to an alkynylated biolomolecule (protein, peptide, nucleic acid, glycan, etc.) or advanced material, it can act as a 19F NMR sensor of its surroundings or sense the interactions with transition metals. .
Despite the relatively low 19F NMR integration intensity, it can be beneficial in cases where organic cosolvents should be avoided or aqueous solubility of the resulting conjugate must not be compromised or should be improved or where transition metal coordinating ability is required..
